DeepForest: Sensing Into Self-Occluding Volumes of Vegetation With Aerial Imaging
Summary: Below-canopy volumetric vegetation data is essential for understanding ecosystem dynamics, but traditional remote sensing methods have limited penetration into dense canopy layers. Researchers have developed an approach that utilizes conventional aerial imagery and synthetic-aperture imaging with drones to capture deeper vegetation structures. Pre-trained 3D convolutional neural networks process volumetric reflectance stacks, reducing out-of-focus noise and enhancing structural detail. This multi-spectral method enables a comprehensive analysis of plant health, growth patterns, and environmental conditions across the entire vegetation volume.
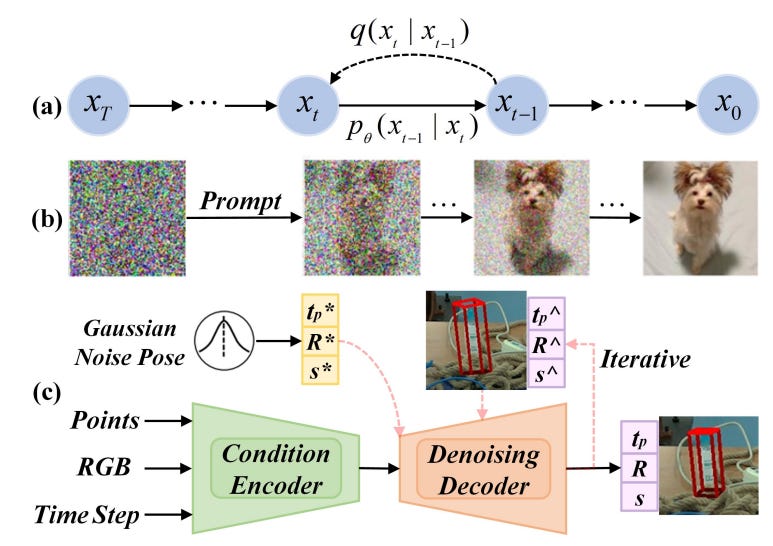
Diff9D: Diffusion-Based Domain-Generalized Category-Level 9-DoF Object Pose Estimation
Summary: Nine-degrees-of-freedom (9-DoF) object pose and size estimation is essential for augmented reality and robotic manipulation, yet existing category-level methods rely on extensive manual data collection. Researchers have introduced a diffusion-based approach that enables domain-generalized 9-DoF object pose estimation by leveraging the latent generalization ability of diffusion models. Trained solely on synthetic data, this method eliminates the need for 3D shape priors and achieves near real-time performance using a reverse diffusion process. Experimental results on benchmark datasets and a real-world robotic system demonstrate state-of-the-art domain generalization capabilities.
FinRLlama: A Solution to LLM-Engineered Signals Challenge at FinRL Contest 2024
Summary: In response to Task II of the FinRL Challenge at ACM ICAIF 2024, researchers propose a novel prompt framework for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with Reinforcement Learning from Market Feedback (RLMF). The framework integrates market-specific features and short-term price dynamics to enhance trading signal precision. By fine-tuning the LLaMA-3.2-3B-Instruct model with historical market data and reward-based feedback, it addresses the contextual limitations of traditional LLMs in financial applications. Experimental results demonstrate superior signal consistency and improved trading outcomes, earning the winning position in Task II.
One Diffusion Step to Real-World Super-Resolution via Flow Trajectory Distillation
Summary: Diffusion models have advanced real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR), but the high computational cost of multi-step models limits their practicality. Researchers propose FluxSR, a one-step diffusion Real-ISR technique based on flow matching models, using FLUX.1-dev as both the teacher and base model. To enhance performance, they introduce Flow Trajectory Distillation (FTD) for distilling multi-step flow models into one-step Real-ISR and employ TV-LPIPS and Attention Diversification Loss (ADL) to mitigate high-frequency artifacts. Experimental results show that FluxSR surpasses existing one-step diffusion-based Real-ISR methods in both quality and efficiency.
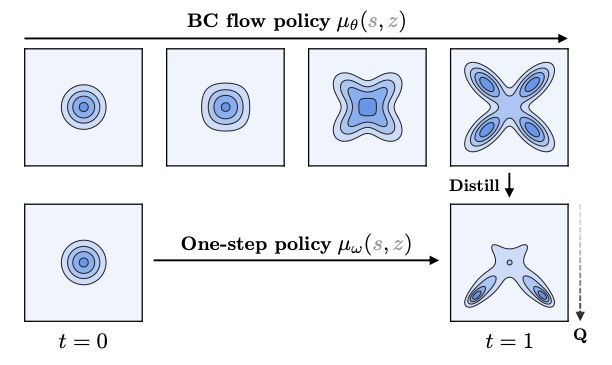
Flow Q-Learning
Summary: Researchers introduce Flow Q-Learning (FQL), a simple yet effective offline reinforcement learning (RL) method that utilizes an expressive flow-matching policy to model complex action distributions. Instead of directly optimizing an iterative flow policy, FQL trains a one-step policy with RL, avoiding unstable recursive backpropagation and reducing inference costs while preserving expressivity. This approach eliminates the need for costly iterative action generation at test time. Experimental results across 73 challenging state- and pixel-based OGBench and D4RL tasks demonstrate strong performance in both offline RL and offline-to-online RL settings.
Love the content? Support my work with a coffee!
Every cup helps me dive deeper into AI research and keep this newsletter running. Your support means the world!